Is it worth strengthening children's immunity in the fall?
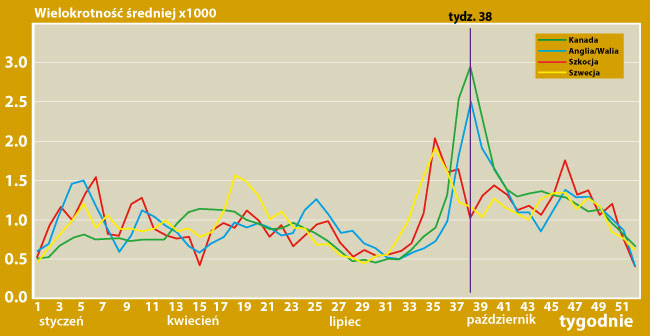
Canadian physicians Malcolm Sears and Neil Johnston analyzed the nature of the autumn asthma exacerbation epidemics from 1990 to 2004. They found that each September, the number of hospitalizations of children due to asthma exacerbations increases sharply. This happened as a result of a very large increase in viral respiratory infections. This is shown in the figure below.
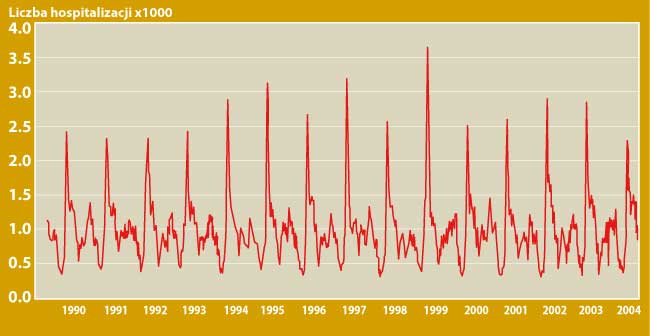
It should be emphasized that similar mass exacerbations have been reported in the USA, England, Mexico, Israel, Finland, Trinidad and Canada, where 20-25% of all asthma exacerbations in children that require hospitalization occur in September. It should be emphasized that 3 weeks after starting school in September, schoolchildren not only experience exacerbations of asthma, but also massive respiratory infections. These are viral infections, which in children without asthma, have the character of "common cold" and are usually not recorded in the statistics.
DATA SOURCES
Over the past several years, the authors have collected data from various sources related to hospitalization to investigate the nature of September asthma exacerbations in children. Data on all respiratory hospital admissions were obtained from the Canadian Institute for Health Information (1990-2004; Center for Epidemiology of the Swedish National Committee for Health and Welfare (1992-2002) and the Medical Statistics Unit of Imperial College, London, UK Britain (1990-2002).
THE ASTHMA OUTBREAK AND BACK TO SCHOOL
The peak of mass hospitalizations for asthma in children in Canada is synchronized with the return of the summer holidays. Every year between 1990 and 2004, the peak incidence occurred in week 38 (third week of September), with the exception of 1992 (week 39) and 1997 and 2003 (week 37). In 1992, school in Canada started a week later, and in 1997 and 2003 almost a week earlier.
Specific mathematical modeling* was used to assess the exact timing and magnitude of the peak, which revealed that September's peak in children's hospital admissions for asthma exacerbations occurred exactly three weeks after the start of the school year. The result is presented graphically in the figure below.
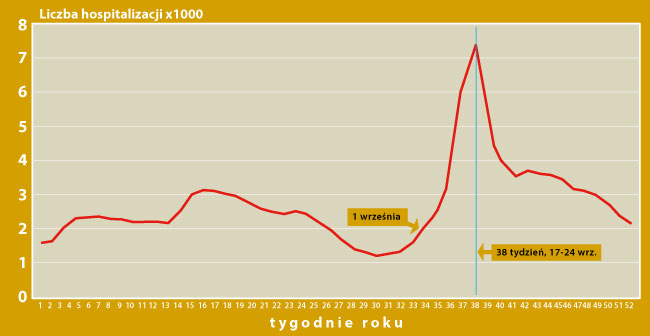
Figure: Using advanced statistical methods, the annual cycles of respiratory infections in children in the period 1990 - 2004 were aggregated into a summary graph showing one aggregated year, broken down into individual weeks. This allows to trace the characteristics of changes in the number of hospitalizations in individual weeks of such a statistical year.
Massive cases, although to a lesser extent, were also observed in preschool children, with a peak 1.7 days later. School-age children not only show the earliest peak of the epidemic, but also its greatest amplitude, suggesting that they are the first to get sick and then transmit asthma exacerbations to older and younger family members. The peak of incidence appeared earliest in 6-year-old children and gradually decreased with a decrease and/or increase in age. Children aged 6 - 7 turned out to be most seriously affected by the epidemic, which should be associated with the fact that it is in this age group that children start school education.
* Mathematical modeling was used, the principles of which are presented in the paper: Johnston et al, The September epidemic of asthma hospitalization: School children as disease vectors J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006,117:557-62
THE ETIOLOGY OF THE EPIDEMIC OF ASTHMA EXTRACTIONS
Inhalant allergens, air pollution and their interaction with the climate have an impact on asthma exacerbation. However, Sears and Johnston believe that returning to school is the decisive factor in asthma exacerbations, which is supported by the exceptionally consistent timing of the peak of exacerbations relative to the start of the school year. Viral infections, especially rhinovirus infections, have been shown to be associated with about 80% of asthma exacerbations in this age group in the early fall.
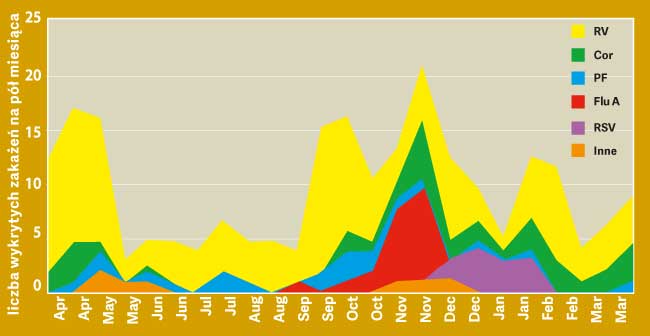
Figure: Number and etiology of detected viral infections during the year, broken down into half-monthly periods. Legend: RV - rhinoviruses, Cor - coronaviruses, PF - para-influenza viruses, Flu-A - influenza A viruses, RSV - respiratory syncytial virus = RS viruses.