Antigen Presentation
Antigen presentation - a term encompassing immune mechanisms that involve "showing" the antigen to T lymphocytes with the participation of MHC molecules. The main goal of antigen presentation is to develop a specific response to a given antigen. It is characteristic that antigens are not presented in their original (native) form, but in a processed form.
There are three classes of MHC that differ in their functions:
• MHC class I – are found on all nucleated cells and participate in defense against intracellular pathogens.
• MHC class II – occurs on antigen-presenting cells
• MHC class III – are various molecules unrelated to the antigen presentation process.
They were first designated as probable presenting molecules due to their location between the MHC class I and MHC class II genes (which was rejected after further genome studies). While there are outstanding structural similarities between classes I and II, class III MHCs are not similar to the other two classes or to each other.
Human MHCs are called HLA – human leukocyte antigens.
Diversity of antigen presentation, mediated by MHC* classes I and II, is attained in three ways: (1) the MHC's genetic encoding is polygenic, (2) MHC genes are highly polymorphic and have many variants, (3) several MHC genes are expressed from both inherited alleles.
- Class I of MHC molecules, which present antigens to Tc cells (cytotoxic lymphocytes), are involved in defense against intracellular pathogens, e.g. viruses. If such an antigen is recognized as foreign, the presenting cell will be killed, because its presence on the MHC class I molecule indicates the existence of the pathogen inside the cell. When killing a cell, a Tc lymphocyte usually also kills the parasite inside it. It can be said that in this way the individual (cell) is sacrificed for the common good (whole organism).
- Class II of MHC molecules that present antigens to Th cells (helper lymphocytes) do not cause the death of the antigen-presenting cell. In this case, this cell starts secreting cytokines that stimulate the Th lymphocytes. Th lymphocytes are important cells that regulate the immune response. Thanks to this, class II of MHC molecules participate in the stimulation of other cells via helper T cells.
- Cross-presentation is a mechanism that enables the stimulation of both Th cells and Tc cells, involving both class I and class II of MHC molecules. However, it is not a simple combination of the two previously mentioned types of antigen presentation. It occurs in a characteristic way with the participation of specific cells that present antigens simultaneously on MHC of both classes and are not killed by Tc lymphocytes.
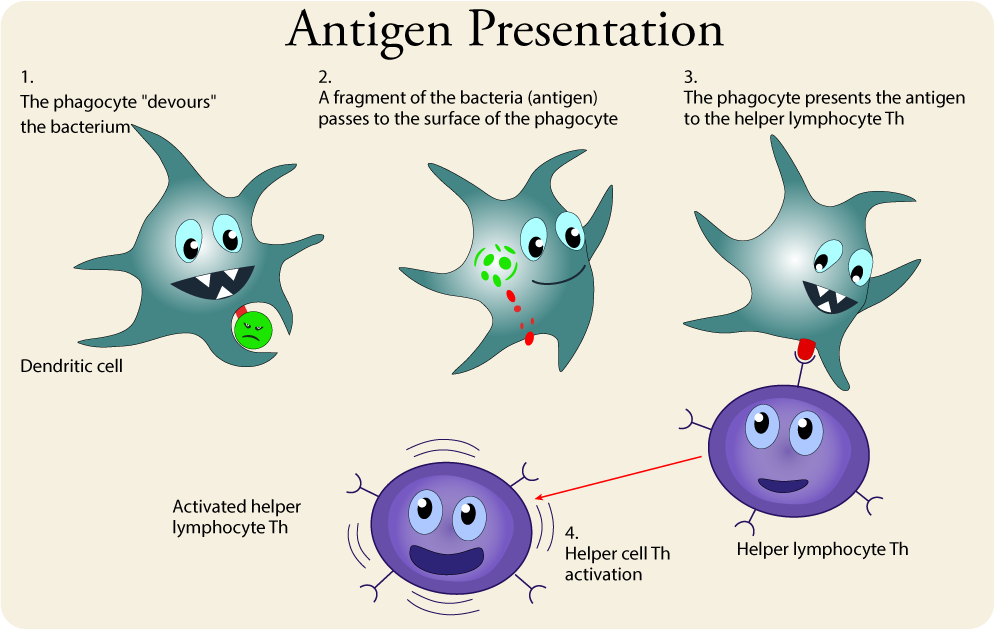
2 Macrophages and dendritic cells belong to the so-called antigen presenting cells.