T Lymphocytes
T lymphocytes (T cells) form two main and distinct groups: T helper lymphocytes and T killer lymphocytes. The name T lymphocytes comes from the Latin name of the thymus – thymus – a gland located behind the sternum. T lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow and then migrate to the thymus where they mature.
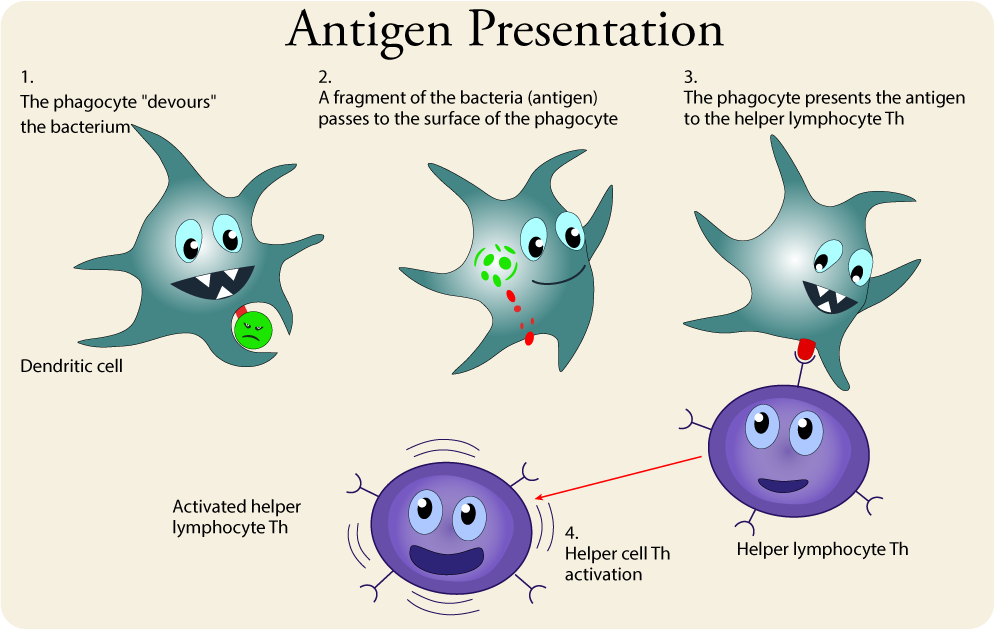
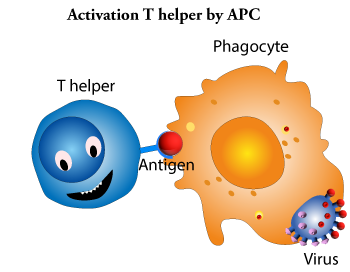 Th helper lymphocytes are the main driving force and regulator of the immune system. Their primary task is to activate B lymphocytes and killer T lymphocytes. However, the Th helper cells themselves must be activated first. This happens when a macrophage or dendritic cell that has previously absorbed the intruder moves to a nearby lymph node and presents information about the caught pathogen. The phagocyte presents a fragment of the intruder's antigen on its surface in a process known as antigen presentation. A Th helper cell is activated when its receptor recognizes an antigen. Once activated, the Th helper cell begins to divide and produce proteins that activate B and T cells as well as other cells of the immune system.
Th helper lymphocytes are the main driving force and regulator of the immune system. Their primary task is to activate B lymphocytes and killer T lymphocytes. However, the Th helper cells themselves must be activated first. This happens when a macrophage or dendritic cell that has previously absorbed the intruder moves to a nearby lymph node and presents information about the caught pathogen. The phagocyte presents a fragment of the intruder's antigen on its surface in a process known as antigen presentation. A Th helper cell is activated when its receptor recognizes an antigen. Once activated, the Th helper cell begins to divide and produce proteins that activate B and T cells as well as other cells of the immune system.
Antigen Presentation
The presentation of antigens is the task of antigen presenting cells. These include phagocytes, primarily dendritic cells (derived from macrophages) and macrophages. Their main task is to present the collected antigens. These cells present foreign antigen to other immune cells, and secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines that attract cells of the adaptive immune response.
Natural Killer Cells (NK cells) specialize in attacking body cells infected with viruses and sometimes bacteria. It also attacks cancer cells. The killer T cell has receptors that look for any matching cell. If a cell is infected, it quickly dies. Infected cells can be recognized by tiny traces of the intruder - the antigen that can be detected on their surface.
B Lymphocytes
The B cell (B Lymphocyte) searches for an antigen that matches its receptors. If it finds such an antigen, it attaches to it and a trigger signal is activated inside the B lymphocyte. But to be fully activated, the B lymphocyte also needs a protein produced by Th helper lymphocytes. When this happens, the B lymphocyte begins to divide, producing its own cell clones, and during this process, two new types of cells are created: plasma cells and memory B lymphocytes.
The plasma cell is specialized in producing specific proteins called antibodies that will act on an antigen that fits the B cell receptor. Antibodies released by plasma cells can seek out "intruders" and help destroy them. Plasma cells produce antibodies at an extraordinary rate and can release tens of thousands of antibodies per second. When Y-shaped antibodies encounter a matching antigen, they attach to it. The attached antibodies serve as a "tasty coating" for feeding cells such as macrophages. Antibodies also neutralize toxins and disable viruses, preventing them from infecting new cells. Each arm of the Y-shaped antibody can attach to a different antigen. So when one arm attaches to one antigen on one cell, the other arm can attach to another cell. In this way, pathogens are gathered into larger groups, which are easier for phagocytosing cells. In addition, bacteria and other pathogens covered with antibodies are easier targets for attack by complement system proteins.
Memory B cells Memory lymphocytes can recognize an antigen introduced into the body during a prior infection or vaccination. Memory lymphocytes mount a rapid and strong immune response when exposed to an antigen for a second time. Both T lymphocytes (T cells) and B lymphocytes (B cells) can become memory cells.
Figure 1: B-cell–T-cell interactions.The two-way interaction between B cells and T cells provides the basis for the concept that, in certain autoimmune diseases, an amplification cycle might allow persistent immunopathology to arise from a minor 'trigger' factor. Such a trigger might initiate the cycle through events in either the B-cell or the T-cell compartment, including the stochastic generation of both B-cell receptors (BCRs) and T-cell receptors (TCRs).
Innate Immunity and Adaptive Immunity
Innate immunity is the body's first line of defence against pathogens. It is general and non-specific, which means it does not differentiate between types of pathogens. Adaptive immunity is a type of immunity that is built up as we are exposed to diseases or get vaccinated.
Innate immunity, also known as genetic or natural immunity, is immunity that an organism is born with. This type of immunity is written in one’s genes, offering lifelong protection. It is considered the more evolutionarily primitive immune system and consequently, as well as being found in vertebrates, is also found in various shapes and forms in plants, fungi and insects. The innate immune response is fast acting and non-specific, meaning it does not respond differently based on the specific invader that it detects.
We are not born with adaptive immunity and it is not “hard wired” in their genes like innate immunity. It is acquired during their lifetime as a result of exposure to specific antigens, be that through natural means such as infection or by vaccination. Consequently, it is also known as acquired immunity. An adaptive immune response is much slower than an innate response, taking days or even weeks to develop on first encounter (the primary immune response), but is specific to the antigen(s) present and can retain a long term “memory” to enable a faster response if it is encountered again in the future. Adaptive immunity does it necessarily last throughout an organism’s entire lifespan, especially if it is not regularly re-exposed, although it can.
| Innate Immmunity (Nonspecific) | Adaptive Immunity (Specific) |
|---|---|
| Nonspecific responce | Specific responce to pathogens and antigens |
| Exposure leads to a complete and maximum response | Delay between exposure and complete response |
| Cellular and humoral components | Cellular and humoral components |
| Lack of immunological memory | Exposure leads to the development of immunological memory |
| It occurs in almost all forms of life | It occurs in vertebrates |